Looking for Global training? Go to https://firebrand.training/en or stay on the current site (United Kingdom)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Please read our full terms and conditions.
6.3 Sequence Activities
"The process of identifying and documenting relationships among the project activities."
The definition shown above in italics is taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
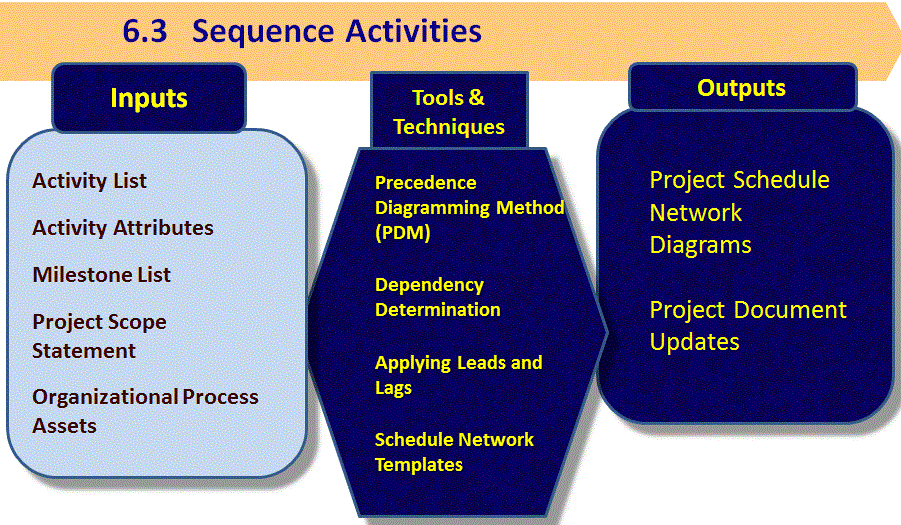
Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013 Figure 6-7 Page 153
Defines the logical sequence of work which elicits the best efficiency taking all project constraints into account
Milestones:
- Major interfaces between phases
- Typically on the critical path to track significant deliverables
- Significant achievements
- Structure reporting process
- Provide feedback to the team
Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM)
Produces a project schedule network diagram
- Also called Activity on Node – detail is in the Node rectangle
- Using rectangular boxes (nodes), to represent activities
- And arrows between them, to represent precedence relationships.
- Shows the Critical Path, using the Critical Path Analysis Method
- May also get reference to Activity on Arrow – ADM – Arrow Diagramming Method. This is very rarely used
Four Types of Relationship
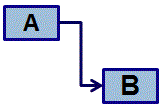
Finish-to-Start (FS) - Activity A must finish before activity B can start.
Example: For a new kitchen installation - when laying tiles we must finish putting the adhesive on the wall before putting the tile on the adhesive
Finish-to-Finish (FF) - Activity A must finish before activity B can finish.
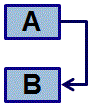
Example: We must put all the tiles on the wall before we can complete putting all the spacers in between.
Start-to-Start (SS) - Activity A must start before activity B can start.
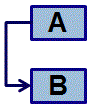
Example: We must start install the base units before we can fit the worktops.
Start-to-Finish (SF) - Activity A must start before activity B can finish.
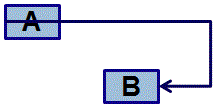
Example: We have to get the electrician to fit the grounding earth wire to the pipework before the kitchen can be completed
Leads and Lags
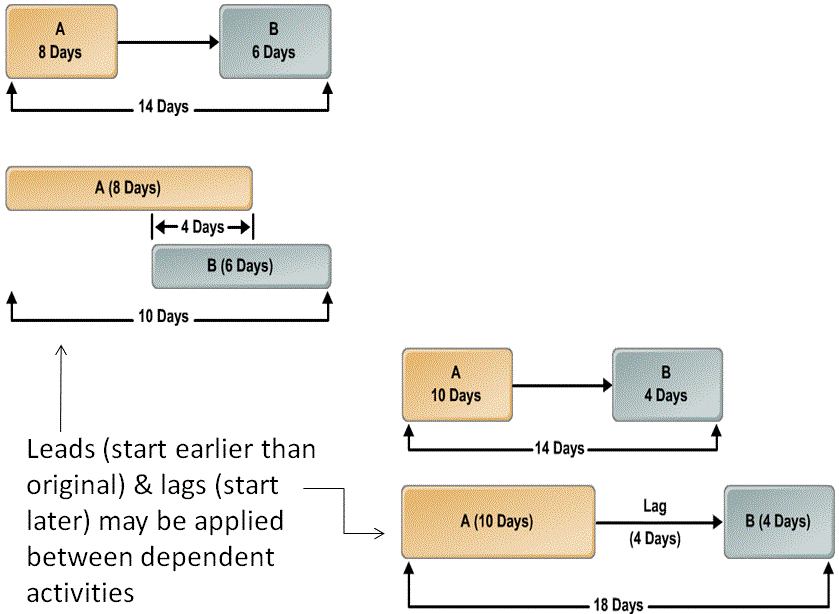
Different Types of Dependency
Mandatory
- Inherent to the work itself and is usually affected by physical constraints
- Example – need to have the trench depth inspected and passed before concrete can be laid in it
Discretionary
- Defined by the project and project management team at their discretion.
External
- Contingent on inputs from outside the project activities.
Internal
- In the team‟s control
Precedence Diagramming Method
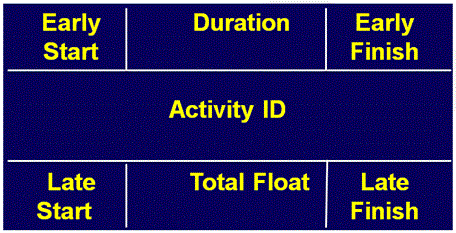
- ID - Identifier
- ES - Earliest Start
- LS - Latest Start
- TF - Total Float (Slack in the activity/task)
- D - Duration
- EF - Earliest Finish
- LF - Latest Finish
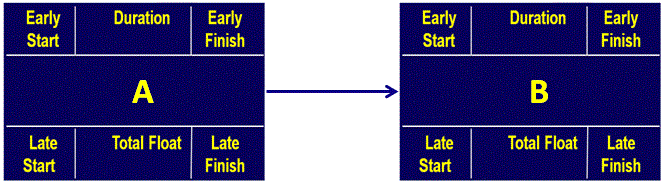
Critical Path: Related terms
Early Start - "the earliest date that uncompleted activities can be started given the network logic and any schedule constraints&"
Early Finish - "the earliest date that uncompleted activities can be finished"
Late Start - "the latest date that an activity can begin without compromising a specified milestone e.g. project finish date"
Late Finish - "the latest date than an activity can finish without compromising a specified milestone"
The definitions shown above in italics are taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
A Question of Float
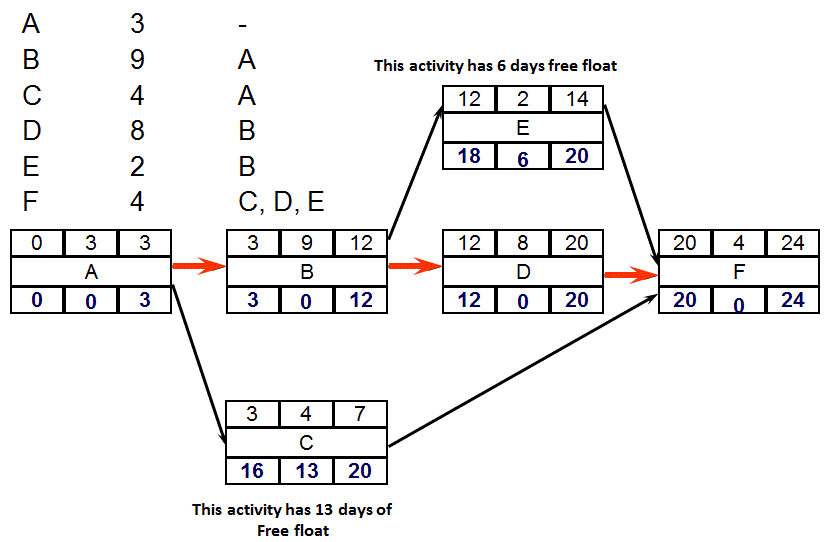
Total Float - "the time an activity can be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project finish date"
Free Float - "amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the early start of any dependent following activity";
Formula to calculate Slack or Total Float:
= Late Finish - Early Finish, or Late Start - Early Start
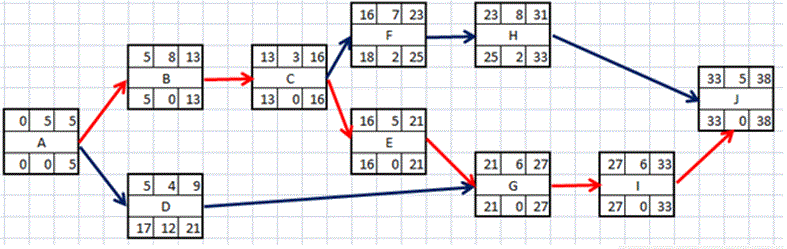
You are given a Network Diagram showing:
Free Float = ES of B – EF of A
The definitions shown above in italics are taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, (PMBOK® Guide) – Fifth Edition, Project Management Institute Inc., 2013
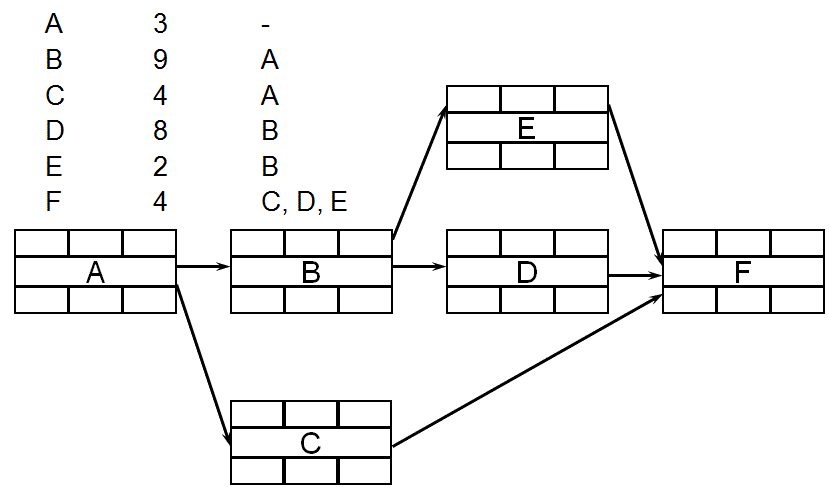
PDM – Draw Nodes and Dependencies
PDM - Durations
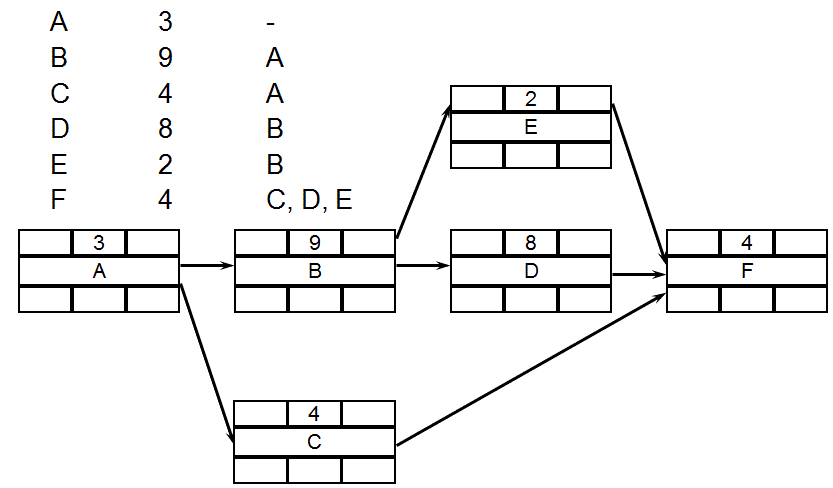
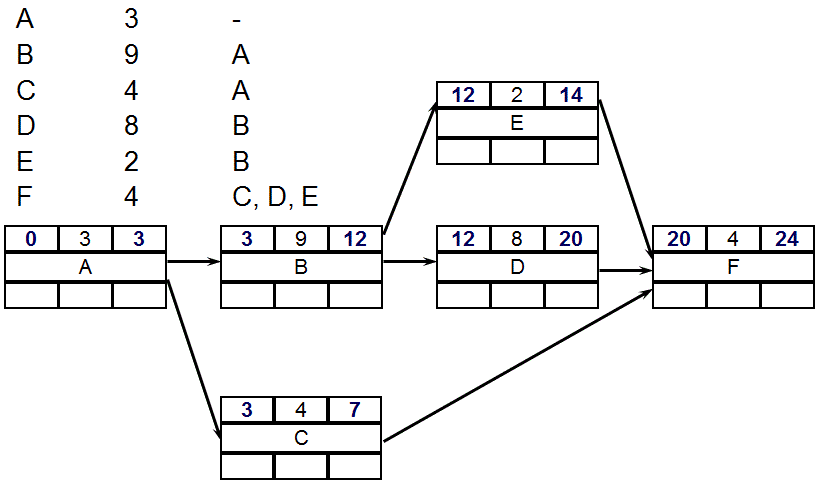
PDM - Forward Pass
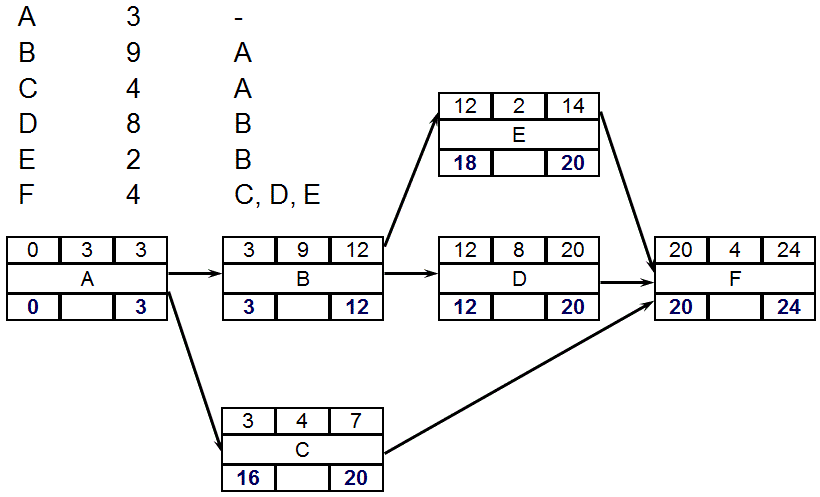
PDM - Backward Pass
PDM - Calculate Float and its type
Exercise on PDM
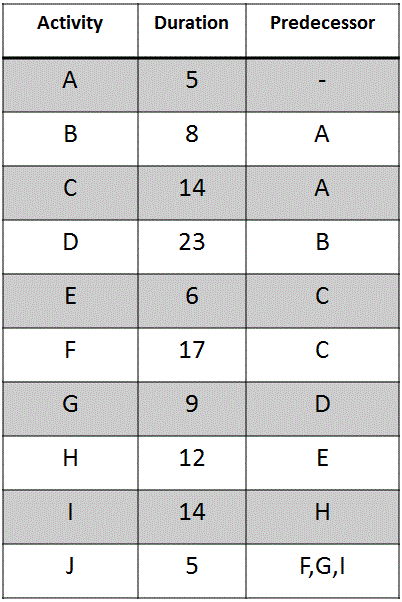
- Draw the network diagram
- Find the critical path
- What is the duration of all of the critical activities added together?
- What type of float do activities B and D have?
You could get 5 questions requiring you to draw a network diagram to be able to answer the question
Note – the same information may be used on different questions!!
PDM Exercise Answer
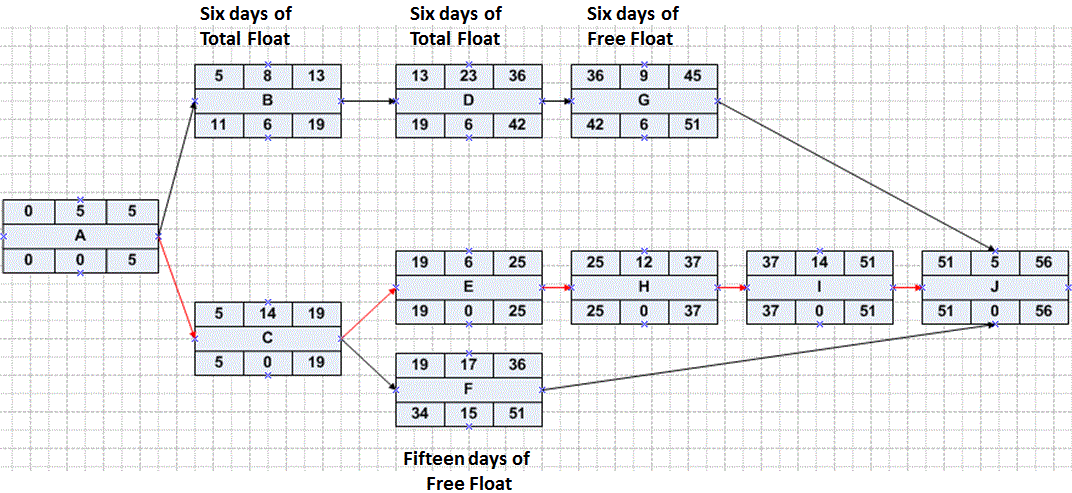
Another Exercise
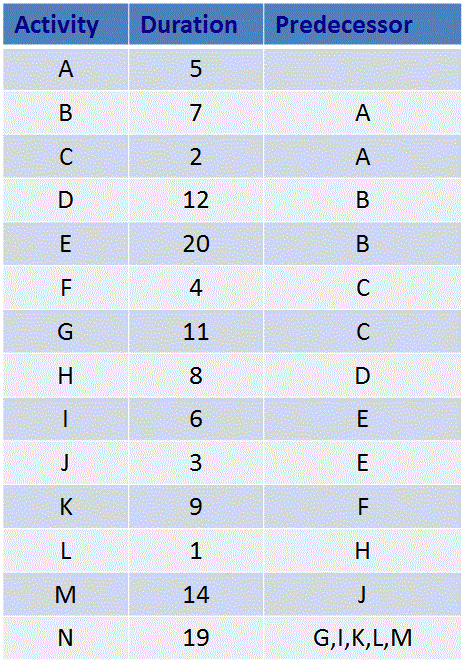
- What is the duration of the critical path?
- Which activities have total float?
- Which activities have free float?
Exercise Answer
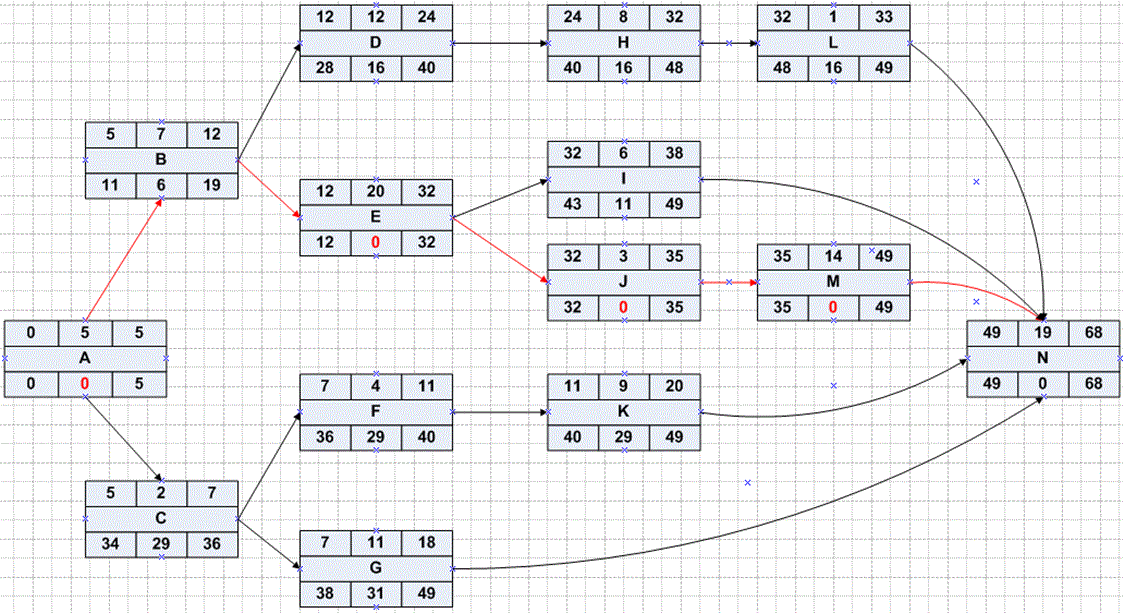
Exceptions
GERT (Graphical Evaluation and Review Technique): is a network diagram which allows for conditional branches and loops and multiple project ends (rarely appears in the exam)
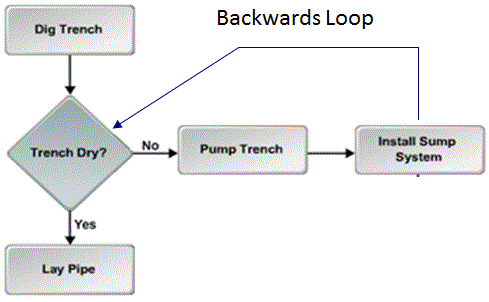
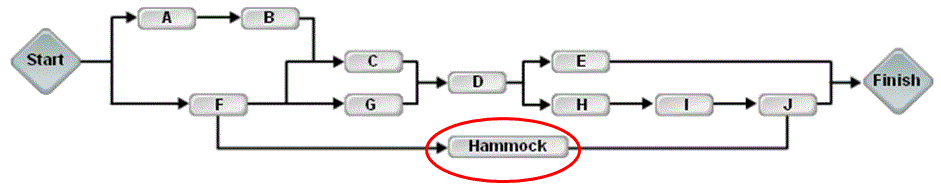
Hammock activity: a group of related schedule activities that, for reporting purposes, is shown as a single aggregate activity in a bar chart or graph.
DISCLAIMER
Firebrand Training grants you a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to access and use the site. You may download or print material from the site only for your own personal, non-commercial use. Read our full terms and conditions on https://firebrand.training/uk/learn/terms-and-conditions.
 Part of the BPP Education Group
Part of the BPP Education Group